Is An Animal Cell Eukaryotic Or Prokaryotic
Chapter 3: Introduction to Jail cell Structure and Role
3.2 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
By the end of this section, yous volition exist able to:
- Name examples of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms
- Compare and dissimilarity prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells
- Describe the relative sizes of different kinds of cells
Cells fall into one of two wide categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. The predominantly single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea are classified every bit prokaryotes (pro– = before; –karyon– = nucleus). Animal cells, institute cells, fungi, and protists are eukaryotes (eu– = true).
Components of Prokaryotic Cells
All cells share four common components: 1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the jail cell's interior from its surrounding environment; two) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell in which other cellular components are found; 3) DNA, the genetic material of the prison cell; and 4) ribosomes, particles that synthesize proteins. Nevertheless, prokaryotes differ from eukaryotic cells in several ways.
A prokaryotic cell is a simple, single-celled (unicellular) organism that lacks a nucleus, or any other membrane-jump organelle. We will shortly come to run into that this is significantly different in eukaryotes. Prokaryotic Deoxyribonucleic acid is institute in the central part of the jail cell: a darkened region chosen the nucleoid.
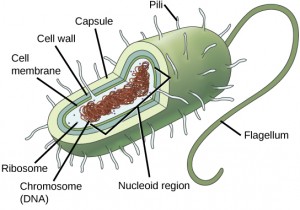
Unlike Archaea and eukaryotes, leaner have a prison cell wall made of peptidoglycan, comprised of sugars and amino acids, and many have a polysaccharide capsule (Effigy three.vi). The cell wall acts equally an extra layer of protection, helps the prison cell maintain its shape, and prevents dehydration. The capsule enables the prison cell to attach to surfaces in its environment. Some prokaryotes have flagella, pili, or fimbriae. Flagella are used for locomotion, while virtually pili are used to substitution genetic fabric during a type of reproduction called conjugation.
Eukaryotic Cells
In nature, the human relationship between form and function is apparent at all levels, including the level of the cell, and this will become articulate as we explore eukaryotic cells. The principle "form follows function" is constitute in many contexts. For example, birds and fish have streamlined bodies that allow them to move quickly through the medium in which they alive, be information technology air or water. It means that, in full general, i can deduce the function of a structure past looking at its course, considering the two are matched.
A eukaryotic cell is a cell that has a membrane-jump nucleus and other membrane-bound compartments or sacs, chosen organelles, which have specialized functions. The word eukaryotic means "true kernel" or "true nucleus," alluding to the presence of the membrane-spring nucleus in these cells. The word "organelle" means "little organ," and, every bit already mentioned, organelles have specialized cellular functions, just as the organs of your body accept specialized functions.
Jail cell Size
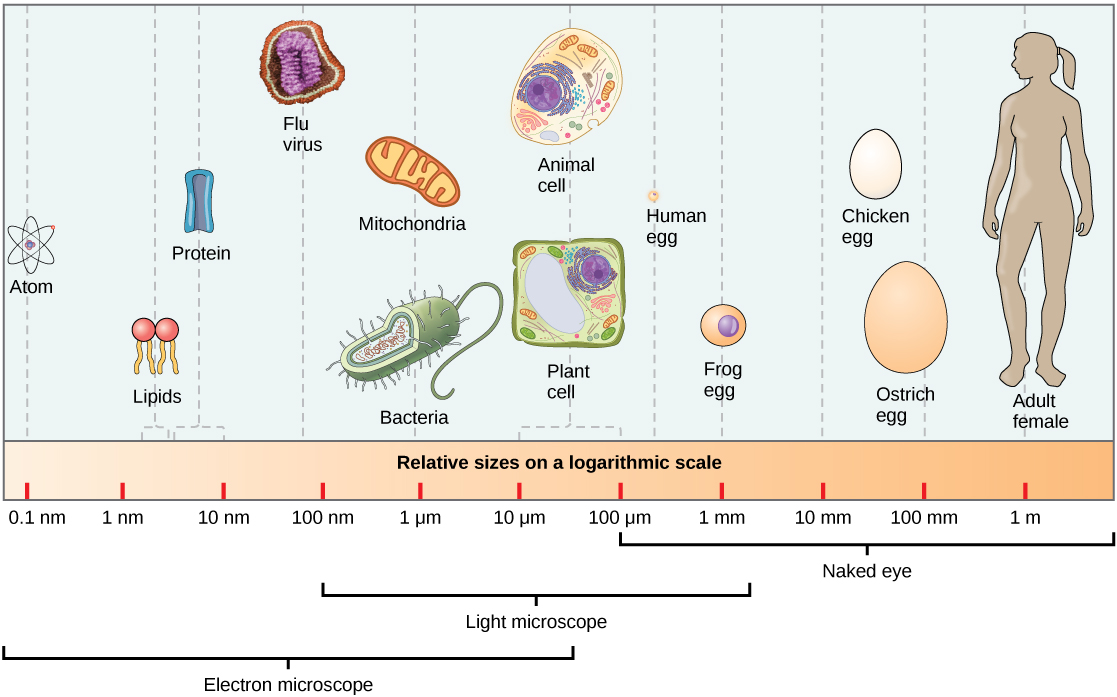
At 0.1–5.0 µm in diameter, prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which have diameters ranging from 10–100 µm (Figure three.7). The small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly spread to other parts of the cell. Similarly, whatever wastes produced within a prokaryotic cell can rapidly move out. However, larger eukaryotic cells accept evolved different structural adaptations to enhance cellular ship. Indeed, the large size of these cells would non be possible without these adaptations. In full general, cell size is express because book increases much more speedily than does jail cell surface area. Every bit a jail cell becomes larger, it becomes more and more difficult for the prison cell to acquire sufficient materials to support the processes inside the cell, because the relative size of the surface expanse beyond which materials must exist transported declines.
Section Summary
Prokaryotes are predominantly unmarried-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea. All prokaryotes have plasma membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, a jail cell wall, DNA, and lack membrane-leap organelles. Many likewise accept polysaccharide capsules. Prokaryotic cells range in diameter from 0.1–5.0 µm.
Like a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes, just a eukaryotic prison cell is typically larger than a prokaryotic cell, has a true nucleus (meaning its Dna is surrounded by a membrane), and has other membrane-leap organelles that let for compartmentalization of functions. Eukaryotic cells tend to exist 10 to 100 times the size of prokaryotic cells.
eukaryotic jail cell: a cell that has a membrane-bound nucleus and several other membrane-spring compartments or sacs
organelle: a membrane-jump compartment or sac inside a prison cell
prokaryotic jail cell: a unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus or any other membrane-leap organelle
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/biology/chapter/3-2-comparing-prokaryotic-and-eukaryotic-cells/
Posted by: kiddmembech.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is An Animal Cell Eukaryotic Or Prokaryotic"
Post a Comment